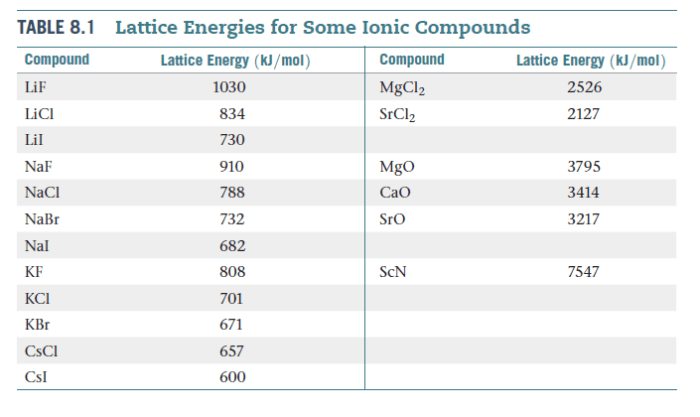
Rank the following ionic compounds by lattice energy: the quest to determine the stability of ionic compounds begins here. Lattice energy, a measure of the strength of the electrostatic forces holding ions together in a crystal lattice, plays a crucial role in understanding the properties and behavior of these compounds.
Delve into the fascinating world of ionic compounds, where the interplay of ionic charge, radius, and electronegativity dictates their lattice energy. Discover the factors that influence this key property and explore the methods used to rank ionic compounds accordingly. From the Born-Haber cycle to Coulomb’s law, uncover the techniques that unravel the secrets of ionic compound stability.
Ionic Compounds and Lattice Energy: Rank The Following Ionic Compounds By Lattice Energy
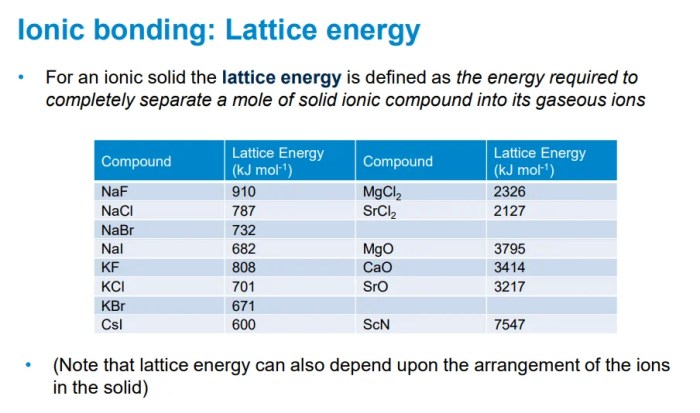
Ionic compounds are formed by the electrostatic attraction between positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). The lattice energy of an ionic compound is the energy required to separate all the ions in one mole of the compound into gaseous ions.
The lattice energy of an ionic compound is directly proportional to the charges of the ions and inversely proportional to the distance between the ions. This relationship is known as Coulomb’s law.
Factors Affecting Lattice Energy, Rank the following ionic compounds by lattice energy
- Ionic charge:The greater the charge of the ions, the greater the lattice energy.
- Ionic radius:The smaller the ionic radius, the greater the lattice energy.
- Electronegativity:The greater the difference in electronegativity between the ions, the greater the lattice energy.
- Polarizability:The more polarizable the ions, the lower the lattice energy.
Methods for Ranking Ionic Compounds
- Born-Haber cycle:The Born-Haber cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that can be used to calculate the lattice energy of an ionic compound.
- Coulomb’s law:Coulomb’s law can be used to calculate the lattice energy of an ionic compound if the charges and distances between the ions are known.
Applications of Lattice Energy
- Predicting the stability of ionic compounds:The lattice energy of an ionic compound can be used to predict its stability. The greater the lattice energy, the more stable the compound.
- Solubility of ionic compounds:The lattice energy of an ionic compound can be used to predict its solubility. The greater the lattice energy, the less soluble the compound.
- Reactivity of ionic compounds:The lattice energy of an ionic compound can be used to predict its reactivity. The greater the lattice energy, the less reactive the compound.
FAQ Guide
What is lattice energy?
Lattice energy is the energy required to separate all the ions in one mole of an ionic compound in its solid state into gaseous ions.
How does ionic charge affect lattice energy?
The greater the charge on the ions, the stronger the electrostatic attraction between them, resulting in higher lattice energy.
What is the role of ionic radius in lattice energy?
Larger ions have lower lattice energy because they are farther apart, weakening the electrostatic attraction between them.