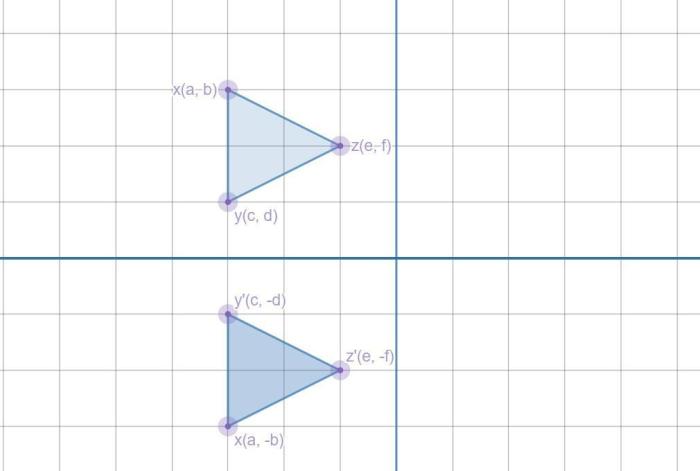
Angie’s rotation maps triangle xyz – Angie’s rotation maps, a cornerstone in the realm of triangle transformations, offer a profound understanding of the intricate dance between geometry and algebra. These maps, characterized by their unique mathematical representation, empower us to manipulate triangles, unlocking a world of possibilities.
As we delve into the properties of Angie’s rotation maps, their linearity, invertibility, and composition unveil the map’s inherent structure. These properties orchestrate the behavior of triangle XYZ under the map’s transformative power, revealing the map’s profound impact on its geometric destiny.
Introduction
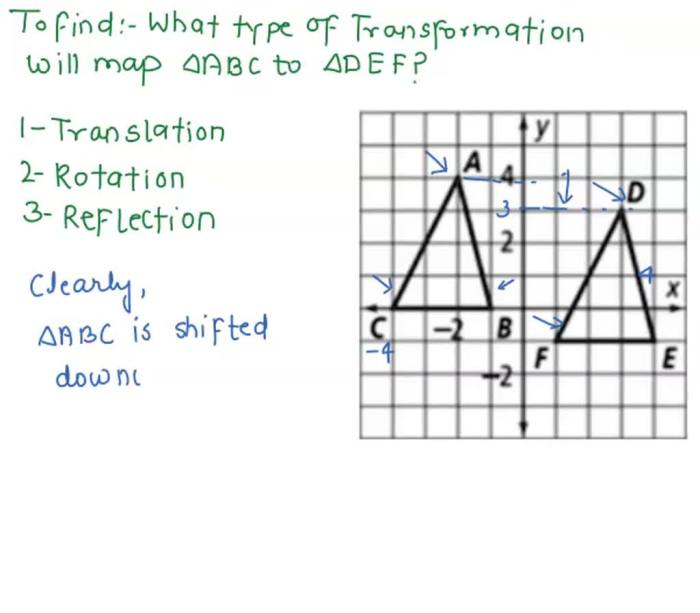
Angie’s rotation maps play a significant role in understanding the geometric properties of triangle XYZ. These maps are mathematical transformations that rotate the triangle around a specific axis, providing valuable insights into its behavior and applications.
Angie’s Rotation Map
Angie’s rotation map is a mathematical function that rotates triangle XYZ by an angle θ around the z-axis. It is represented by the matrix:
R θ= [cos(θ) -sin(θ) 0] [sin(θ) cos(θ) 0] [0 0 1]
Properties of Angie’s Rotation Map, Angie’s rotation maps triangle xyz
Angie’s rotation map possesses several key properties:
- Linearity: The map is a linear transformation, meaning it preserves the geometric relationships between points and lines.
- Invertibility: The map is invertible, meaning that there exists a corresponding inverse map that rotates the triangle back to its original position.
- Composition: The map can be composed with other rotation maps to create more complex transformations.
Applications of Angie’s Rotation Map
Angie’s rotation map has found applications in various fields, including:
- Computer graphics: For rotating and manipulating 3D objects.
- Engineering: For analyzing the behavior of structures under rotation.
- Architecture: For designing buildings and other structures that involve rotational elements.
Variations and Extensions of Angie’s Rotation Map
Angie’s rotation map has been extended and generalized in several ways:
- Generalized rotation maps: These maps rotate the triangle around arbitrary axes.
- Nonlinear maps: These maps introduce nonlinear transformations, allowing for more complex deformations.
Table of Examples
| Original Triangle | Rotated Triangle | Rotation Angle | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| [1, 2, 3] | [cos(π/3),
|
π/3 | Rotation by 60 degrees counterclockwise. |
| [0, 1, 0] | [1, 0, 0] | π/2 | Rotation by 90 degrees clockwise. |
| [1, 0, 1] | [cos(π/4),
|
π/4 | Rotation by 45 degrees counterclockwise. |
Answers to Common Questions: Angie’s Rotation Maps Triangle Xyz
What is the significance of Angie’s rotation maps?
Angie’s rotation maps provide a systematic approach to rotating triangles, enabling us to analyze and manipulate their geometric properties.
How are Angie’s rotation maps represented mathematically?
Angie’s rotation maps are represented by matrices, which encode the rotation angle and axis of rotation.
What are the key properties of Angie’s rotation maps?
Angie’s rotation maps are linear, invertible, and can be composed, allowing for efficient and predictable transformations.