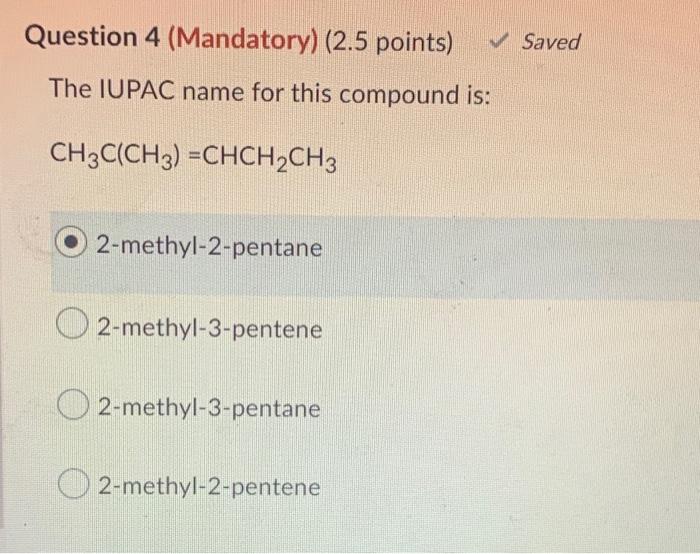
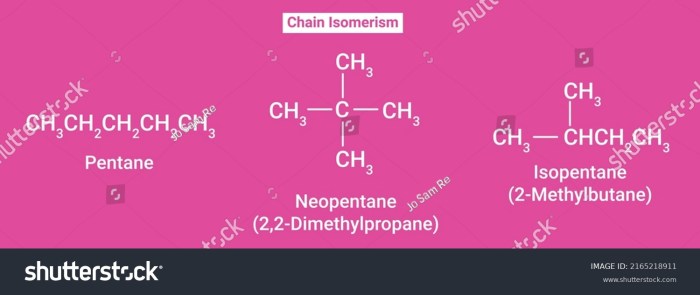
All of the following are representations of 2-methylpentane except embarks on an illuminating journey, delving into the diverse depictions of this organic compound. From intricate structural representations to spectroscopic characterizations, this narrative unravels the complexities of 2-methylpentane with meticulous precision.
As we traverse this scientific landscape, we will encounter various representations of 2-methylpentane, each capturing a distinct aspect of its molecular architecture. These representations serve as invaluable tools for comprehending the physical and chemical properties of this versatile hydrocarbon.
2-Methylpentane: All Of The Following Are Representations Of 2-methylpentane Except
-Methylpentane is a branched hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H14. It is a structural isomer of hexane and has a molecular weight of 86.18 g/mol. 2-Methylpentane is a colorless liquid with a gasoline-like odor. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, and benzene.
Structural Representations
-Methylpentane can be represented by various structural formulas, including:
Lewis structure
CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CH3
Condensed structural formula
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2CH3
Line-angle formula
“` H3C H H H H H | | | | | |CH3-C-C-C-C-C-H | | | | | | H H H H H H“`
Skeletal formula
“`CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH3“`
IUPAC Nomenclature, All of the following are representations of 2-methylpentane except
The IUPAC name for 2-methylpentane is 2-methylpentane. The name reflects the structure of the molecule, which consists of a pentane chain with a methyl group attached to the second carbon atom.
Physical Properties
-Methylpentane has the following physical properties:
Boiling point
60.3 °C
-
Melting point
- 118.5 °C
Density
0.69 g/mL
Chemical Properties
-Methylpentane is a reactive hydrocarbon that undergoes a variety of chemical reactions. Some of the most common reactions include:
Combustion
2-Methylpentane burns in air to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Halogenation
2-Methylpentane reacts with halogens to form alkyl halides.
Alkylation
2-Methylpentane can be alkylated with other hydrocarbons to form branched alkanes.
Spectroscopy
-Methylpentane can be characterized by a variety of spectroscopic techniques. Some of the most common techniques include:
Infrared spectroscopy
The IR spectrum of 2-methylpentane shows a strong absorption band at 2960 cm-1, which corresponds to the C-H stretching vibration.
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
The NMR spectrum of 2-methylpentane shows a singlet at 0.9 ppm, which corresponds to the methyl protons, and a multiplet at 1.3 ppm, which corresponds to the methylene protons.
Mass spectrometry
The mass spectrum of 2-methylpentane shows a molecular ion peak at m/z = 86.
Applications
- -Methylpentane is used in a variety of applications, including:
- As a solvent for paints, varnishes, and lacquers
- As a fuel for internal combustion engines
- As a feedstock for the production of other chemicals
Question & Answer Hub
What is the IUPAC name for 2-methylpentane?
2-Methylpentane
What is the boiling point of 2-methylpentane?
60.3 °C
What are the major applications of 2-methylpentane?
Solvent, fuel additive, and feedstock for chemical synthesis