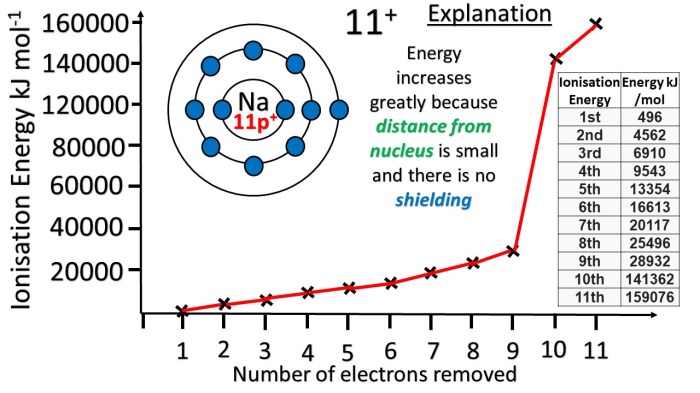
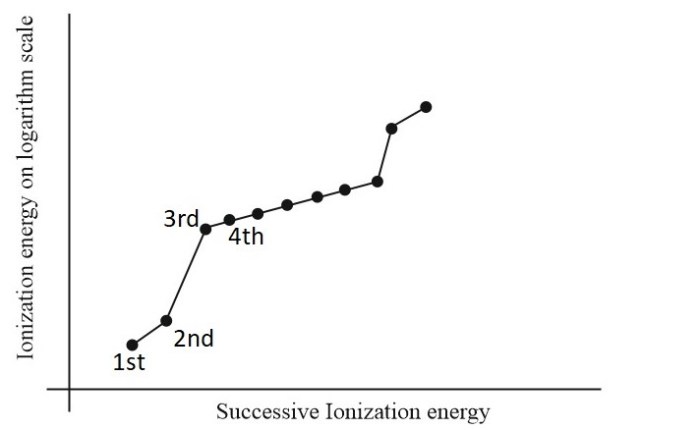
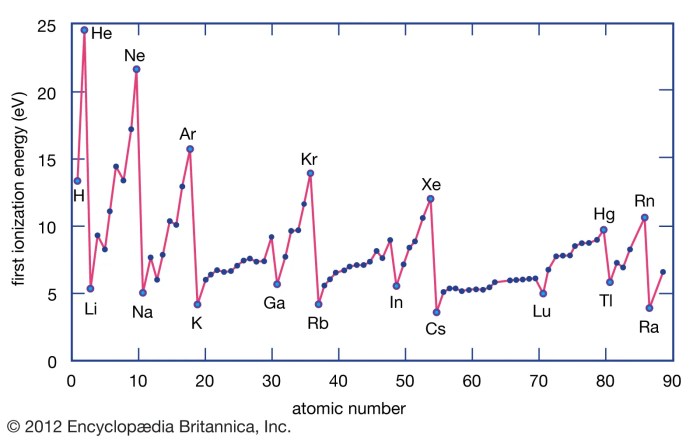
Draw a successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum – The successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum, a visual representation of the energy required to remove electrons from an aluminum atom, offers valuable insights into the electronic structure and properties of this element. This diagram serves as a fundamental tool in chemistry, physics, and materials science, providing a deeper understanding of aluminum’s behavior and applications.
To construct a successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum, one must first grasp the concept of ionization energy and its relation to the element. Ionization energy refers to the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in its gaseous state.
The successive ionization energy diagram depicts the energy required to remove each subsequent electron from the aluminum atom, providing a comprehensive overview of the element’s electronic structure.
Successive Ionization Energy Diagram for Aluminum: Draw A Successive Ionization Energy Diagram For Aluminum
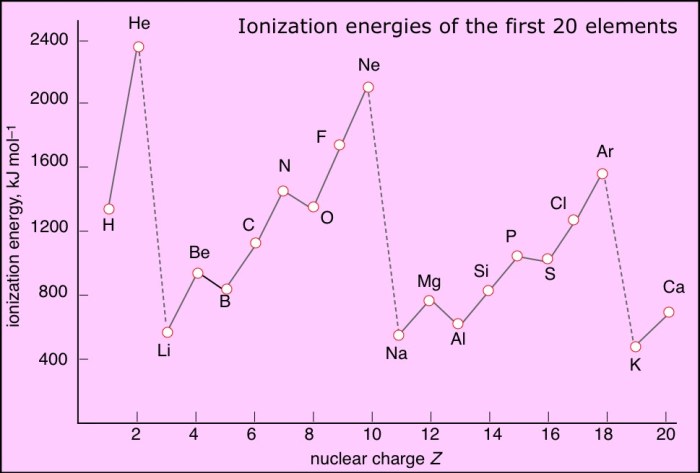
The successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum provides valuable insights into the electronic structure and chemical properties of this element.
1. Successive Ionization Energy Diagram for Aluminum
The successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum represents the energy required to remove electrons from the atom in a step-by-step process. Each ionization energy value corresponds to the energy needed to remove an electron from the outermost energy level of the atom.
Ionization energy is a fundamental property of an element and is influenced by factors such as the atomic radius, nuclear charge, and electron configuration.
2. Creating the Diagram
- Start with the ground-state electron configuration of aluminum: 1s22s 22p 63s 23p 1.
- Calculate the first ionization energy by subtracting the energy of the ground state from the energy of the ion with one electron removed: Al +.
- Repeat the process for subsequent ionization energies, removing one electron at a time: Al 2+, Al 3+, and so on.
- Plot the ionization energies on a graph with the ionization number (the number of electrons removed) on the x-axis and the ionization energy on the y-axis.
3. Interpretation of the Diagram
The successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum shows a gradual increase in ionization energy as more electrons are removed. This is because the remaining electrons experience a stronger electrostatic attraction to the positively charged nucleus as the number of electrons decreases.
The diagram also reveals patterns and trends in the ionization energies. For example, the ionization energy generally increases with the removal of electrons from the same energy level (e.g., 3s electrons) and decreases with the removal of electrons from different energy levels (e.g.,
3p electrons).
4. Comparison with Other Elements
Comparing the successive ionization energy diagrams of aluminum to other elements in the same group (Group 13) or period (Period 3) can provide insights into the periodic trends in ionization energy.
Generally, ionization energy increases across a period (left to right) due to the increasing nuclear charge. Within a group, ionization energy decreases down the group (top to bottom) due to the increasing atomic radius.
5. Applications, Draw a successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum
The successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum finds applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:Understanding the ionization energies of aluminum helps predict its chemical reactivity and bonding behavior.
- Physics:The diagram provides insights into the electronic structure and energy levels of aluminum, which is crucial for understanding its electrical and optical properties.
- Materials science:The ionization energy diagram is used in the design and development of aluminum-based materials with specific properties.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of the successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum?
The diagram provides insights into the electronic structure of aluminum, revealing the energy levels of its electrons and the ease with which they can be removed. It helps understand the chemical reactivity, bonding behavior, and applications of aluminum.
How can the successive ionization energy diagram be used to compare aluminum with other elements?
By comparing the ionization energies of aluminum with those of other elements in the same group or period, scientists can identify similarities and differences in their electronic structures. This comparison aids in understanding periodic trends and the factors influencing ionization energies.
What are some practical applications of the successive ionization energy diagram for aluminum?
The diagram finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and materials science. It helps predict the reactivity of aluminum in chemical reactions, design materials with specific properties, and understand the electronic behavior of aluminum in different environments.