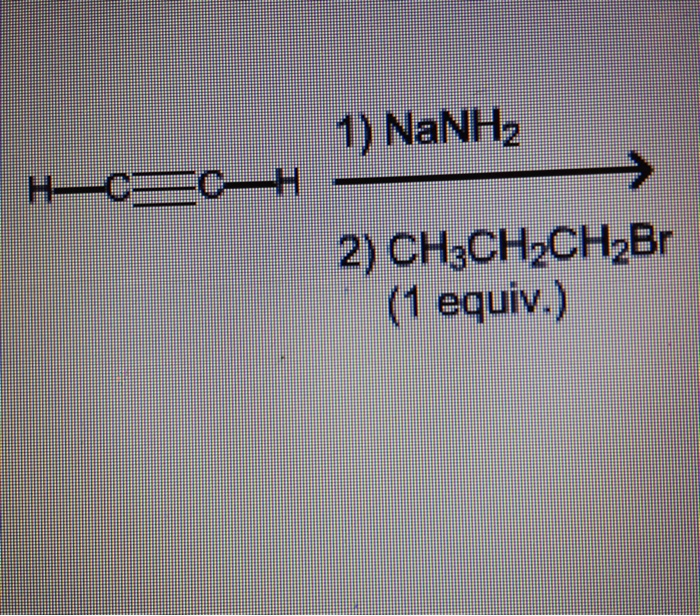
Design a synthesis of 1-butyne from ethyne and ethanol, a pivotal chemical reaction in organic chemistry, takes center stage in this article. We delve into the intricacies of this process, exploring its mechanism, reaction conditions, catalyst selection, and diverse applications.
Brace yourself for a journey that unveils the fascinating world of 1-butyne synthesis, unlocking its potential as a versatile building block in various industries.
Synthesis of 1-butyne
1-butyne is a valuable chemical intermediate used in the synthesis of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and plastics. It can be synthesized from ethyne and ethanol through a catalytic process.
Chemical Reaction
The chemical reaction for the synthesis of 1-butyne from ethyne and ethanol is as follows:
CH≡CH + CH3CH2OH → CH3CH2C≡CH + H2O
The reaction is typically catalyzed by a metal complex, such as palladium or nickel, which facilitates the addition of the ethyne molecule to the ethanol molecule.
Mechanism, Design a synthesis of 1-butyne from ethyne and ethanol
The mechanism of the reaction involves the following steps:
- The catalyst activates the ethyne molecule, forming a metal-ethyne complex.
- The ethanol molecule attacks the metal-ethyne complex, forming a metal-alkoxide complex.
- The metal-alkoxide complex undergoes reductive elimination, releasing 1-butyne and the catalyst.
Reaction Conditions
The optimal reaction conditions for the synthesis of 1-butyne include:
- Temperature: 50-100 °C
- Pressure: Atmospheric pressure
- Solvent: Polar aprotic solvents, such as dimethylformamide (DMF) or dimethylacetamide (DMAc)
The reaction conditions can affect the yield and selectivity of the reaction. Higher temperatures favor the formation of 1-butyne, while lower temperatures favor the formation of byproducts.
Catalyst Selection
The choice of catalyst is crucial for the synthesis of 1-butyne. Different catalysts exhibit different activities and selectivities.
Common catalysts used for this reaction include:
- Palladium complexes
- Nickel complexes
- Copper complexes
Palladium complexes are generally the most active and selective catalysts for this reaction.
Applications of 1-butyne
1-butyne has a wide range of applications in different industries, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Synthesis of anti-inflammatory and anticancer drugs
- Fragrances: Synthesis of floral and fruity fragrances
- Plastics: Synthesis of polybutylene, a lightweight and durable plastic
- Fine chemicals: Synthesis of various specialty chemicals, such as solvents and intermediates
1-butyne is also a potential building block for the synthesis of more complex chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Expert Answers: Design A Synthesis Of 1-butyne From Ethyne And Ethanol
What is the significance of 1-butyne in organic chemistry?
1-butyne is a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of various complex organic molecules. It serves as a versatile building block for the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, polymers, and other functional materials.
How does the choice of catalyst impact the synthesis of 1-butyne?
The selection of an appropriate catalyst is crucial for the efficiency and selectivity of the synthesis. Different catalysts exhibit varying activities and can influence the reaction pathway, affecting the yield and purity of 1-butyne.
What are the potential applications of 1-butyne in different industries?
1-butyne finds applications in diverse industries, including the pharmaceutical industry for drug synthesis, the fragrance industry for the production of aroma chemicals, and the polymer industry as a monomer for the manufacturing of specialty plastics.