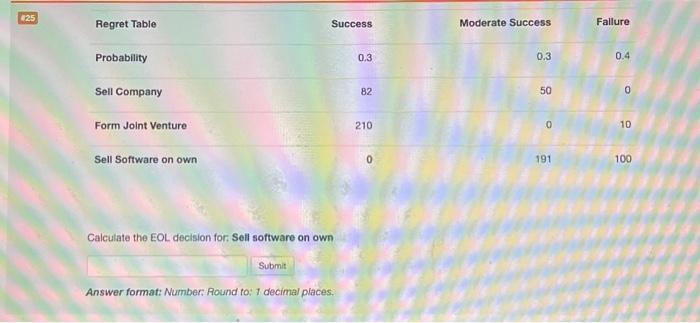
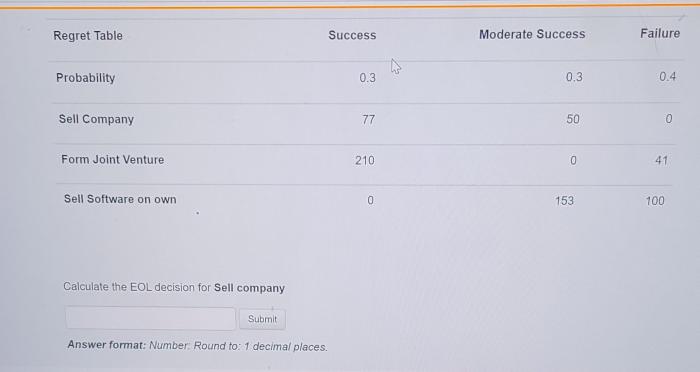
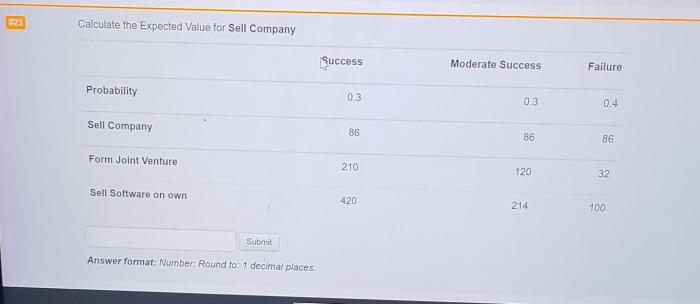
Calculate the EOL decision for sell company delves into the intricate world of company valuation, exit strategies, tax implications, negotiation, due diligence, and post-sale considerations. This comprehensive guide provides invaluable insights for business owners contemplating the sale of their company.
As you embark on this journey, you will gain a thorough understanding of the factors that influence company valuation, the various exit strategies available, and the tax implications associated with each option. We will explore the negotiation process, emphasizing the importance of due diligence and providing tips for securing a favorable deal.
Company Valuation: Calculate The Eol Decision For Sell Company
Company valuation is the process of determining the economic value of a business. It is a crucial step in the exit planning process, as it provides a basis for negotiations and helps ensure that the business is sold at a fair price.
There are a number of different company valuation methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include:
- Asset-based valuation: This method values a company based on the fair market value of its assets.
- Income-based valuation: This method values a company based on its future earnings potential.
- Market-based valuation: This method values a company based on the prices of comparable companies in the same industry.
The choice of which valuation method to use will depend on a number of factors, including the nature of the business, the availability of financial information, and the desired level of accuracy.
Financial statements play a vital role in determining company value. They provide a snapshot of the company’s financial health and performance, and can be used to assess its risks and opportunities. Industry benchmarks and comparable transactions can also be used to support the valuation process.
Exit Strategies
Once a business owner has decided to sell their company, they need to choose an exit strategy. There are a number of different exit strategies available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Sale to a strategic buyer: This involves selling the company to another company in the same industry.
- Sale to a financial buyer: This involves selling the company to a private equity firm or venture capital firm.
- Initial public offering (IPO): This involves selling shares of the company to the public.
- Employee stock ownership plan (ESOP): This involves selling shares of the company to the employees.
The choice of which exit strategy to use will depend on a number of factors, including the size and stage of the business, the owner’s financial goals, and the tax implications.
Tax Implications
The sale of a company can have significant tax implications. The most common tax issue is capital gains tax, which is levied on the profit from the sale of a capital asset. The capital gains tax rate will vary depending on the individual’s tax bracket.
There are a number of strategies that can be used to minimize the tax liability associated with the sale of a company. These strategies include:
- Selling the company in installments
- Using a tax-deferred exchange
- Donating a portion of the proceeds to charity
It is important to consult with a tax advisor to discuss the tax implications of selling a company before making any decisions.
Negotiation and Due Diligence
Once a buyer has been identified, the negotiation process begins. This is a critical stage in the exit planning process, as it is where the final terms of the sale are agreed upon.
It is important to have a strong negotiating team in place, including an attorney, accountant, and financial advisor. The negotiating team should be prepared to discuss a variety of issues, including the purchase price, the terms of payment, and the closing date.
Due diligence is a critical part of the negotiation process. This is where the buyer investigates the company’s financial and legal status. Due diligence can be a lengthy and complex process, but it is essential to ensure that the buyer is fully aware of the risks and opportunities associated with the acquisition.
Post-Sale Considerations
Once the sale of the company is complete, there are a number of post-sale considerations that the seller should be aware of.
- Maintain confidentiality: It is important to maintain confidentiality throughout the sale process and after the sale is complete.
- Protect intellectual property: The seller should take steps to protect the company’s intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
- Transition the business to new ownership: The seller should work with the buyer to ensure a smooth transition of the business to new ownership.
By following these considerations, the seller can help ensure a successful post-sale experience.
FAQ
What is the most important factor to consider when valuing a company?
The financial statements of the company, which provide insights into its financial health and performance.
What are the different types of exit strategies available to company owners?
Sale to a strategic buyer, sale to a financial buyer, initial public offering (IPO), and management buyout.
What are the tax implications of selling a company?
Capital gains tax, which is levied on the profit made from the sale of the company.