Unveiling the intricate beauty of butterflies, this exploration delves into the parts of a butterfly diagram, offering a captivating overview of their anatomy, wings, life cycle, behavior, habitats, and conservation.
As we embark on this journey, let us first examine the essential body parts of a butterfly, their functions, and the fascinating structure and patterns of their wings.
Butterfly Anatomy: Parts Of A Butterfly Diagram
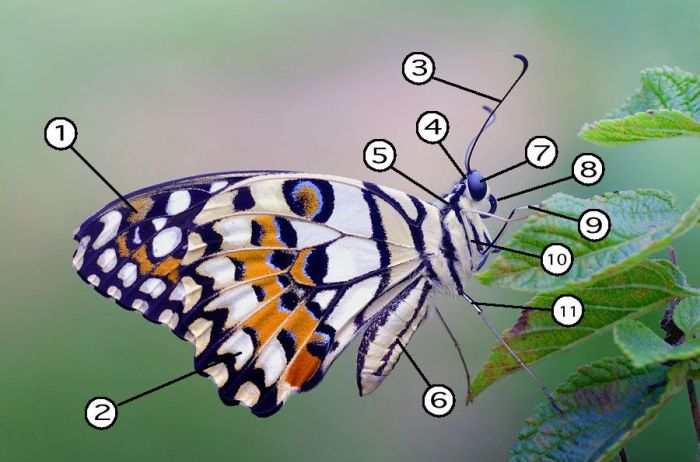
Butterflies are fascinating creatures with unique and intricate body structures. Understanding their anatomy helps us appreciate their beauty and complexity.
Main Body Parts
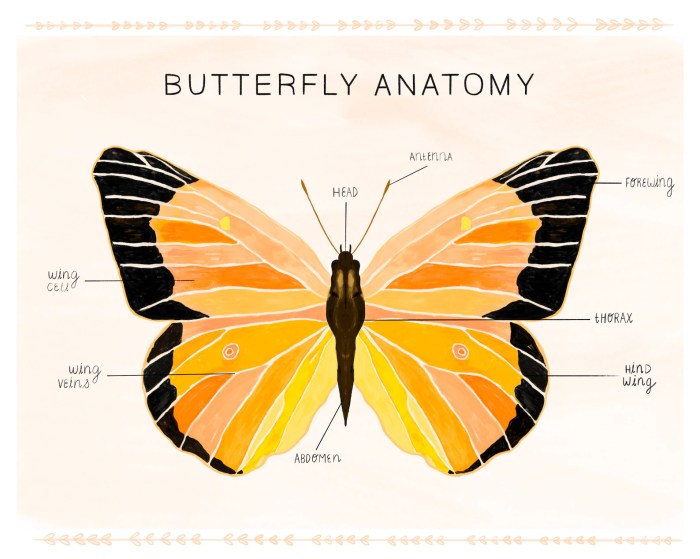
A butterfly’s body consists of three main parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. Each part plays a specific role in the butterfly’s survival and reproduction.
- Head:The head houses the butterfly’s sensory organs, including its eyes, antennae, and mouthparts. The eyes provide vision, while the antennae are used for sensing and smelling. The mouthparts are specialized for feeding on nectar.
- Thorax:The thorax is the middle section of the butterfly’s body. It contains the butterfly’s wings and legs. The wings are used for flight, while the legs are used for walking and perching.
- Abdomen:The abdomen is the largest part of the butterfly’s body. It contains the butterfly’s digestive system, reproductive organs, and muscles.
Butterfly Wings

Butterfly wings are intricate and delicate structures that serve multiple functions. Their primary role is flight, allowing butterflies to navigate their environment with remarkable agility. Wings also play a crucial role in thermoregulation, helping butterflies maintain optimal body temperatures.
Structure and Function of Butterfly Wings
Butterfly wings are composed of two thin, membranous layers covered in tiny scales. These scales, which give butterflies their vibrant colors, are arranged in overlapping rows and help create the wing’s aerodynamic shape. The wings are attached to the thorax and are controlled by a complex system of muscles that enable intricate flight maneuvers.
Types of Wing Patterns and Their Significance
Butterfly wings exhibit a vast array of patterns, each with its own significance. These patterns can serve as camouflage, helping butterflies blend into their surroundings to avoid predators. Other patterns may attract mates or deter predators by mimicking the appearance of poisonous or unpalatable insects.
Examples of Butterflies with Unique Wing Patterns
- Monarch butterflies are known for their distinctive orange and black wings, which serve as a warning to predators that they are poisonous.
- The Blue Morpho butterfly has iridescent blue wings that reflect light in a dazzling array of colors, attracting mates and deterring predators.
- The Owl butterfly has large, eyespot patterns on its wings that resemble owl eyes, potentially startling predators and giving the butterfly an opportunity to escape.
Butterfly Life Cycle
The butterfly’s life cycle is a fascinating process that involves four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Each stage has its unique characteristics and plays a crucial role in the butterfly’s development.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and food availability, significantly influence the butterfly’s development. Temperature affects the rate of development, with warmer temperatures generally leading to faster growth. Humidity influences the egg’s survival and the ability of the larvae to shed their skin.
Food availability is essential for the growth and survival of the larvae, as they feed on specific plants.
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a fundamental process in the butterfly’s life cycle. It involves a series of dramatic physical changes that transform the butterfly from an egg to an adult. During the larval stage, the butterfly feeds and grows, shedding its skin several times.
In the pupal stage, the larva undergoes a complete transformation, developing wings and other adult features. The adult butterfly emerges from the pupa with fully developed wings and reproductive organs, ready to mate and lay eggs.
Butterfly Behavior

Butterflies are fascinating creatures with a rich repertoire of social behaviors and communication strategies. Their interactions and rituals play a crucial role in their survival and reproduction.Butterflies exhibit social behavior within their species, forming loose aggregations and engaging in various social interactions.
They communicate primarily through visual and chemical cues, utilizing their colorful wings and pheromones to convey messages. Courtship rituals among butterflies are elaborate and species-specific, involving intricate dances and displays.
Social Behaviors
Butterflies form loose associations known as “butterfly puddling.” They congregate at specific sites, such as mud puddles or damp sand, to extract essential minerals and salts. These gatherings provide opportunities for social interactions and potential mating encounters.
Communication
Visual cues are vital in butterfly communication. Their brightly colored wings display patterns and markings that serve as visual signals. Butterflies use these patterns to attract mates, warn of predators, or defend their territories.Chemical communication plays a significant role in butterfly interactions.
They release pheromones, chemical substances that carry specific messages. Pheromones can attract mates, repel predators, or mark territories.
Courtship Rituals
Courtship rituals in butterflies vary widely among species. Many butterflies engage in elaborate aerial displays, fluttering their wings and performing specific flight patterns to attract potential mates. Some species also exhibit courtship dances on the ground or vegetation.
Butterfly Habitats
Butterflies are found in a wide variety of habitats around the world, from tropical rainforests to temperate grasslands. Each type of habitat provides unique resources and challenges for butterflies.
Some of the most common butterfly habitats include:
- Forests: Forests provide butterflies with shelter from the sun and wind, as well as a source of food and water. The trees and shrubs in forests also create a microclimate that is ideal for butterflies.
- Grasslands: Grasslands are another common habitat for butterflies. Grasslands provide butterflies with an abundance of food, including nectar from flowers and pollen from grasses. The open spaces in grasslands also make it easy for butterflies to fly and find mates.
- Wetlands: Wetlands are areas of land that are covered in water for at least part of the year. Wetlands provide butterflies with a source of water and food, as well as a place to lay their eggs. The vegetation in wetlands also provides butterflies with shelter from the sun and wind.
Habitat Preservation
Habitat preservation is essential for butterfly populations. When butterflies lose their habitat, they lose their source of food, water, and shelter. This can lead to a decline in butterfly populations and even extinction.
There are a number of things that can be done to preserve butterfly habitats, including:
- Protecting forests and grasslands from development.
- Restoring wetlands that have been drained or filled.
- Creating butterfly gardens in your own backyard.
Climate Change, Parts of a butterfly diagram
Climate change is also having a significant impact on butterfly habitats. As the climate changes, the distribution of plants and animals is changing. This is causing some butterflies to lose their habitat and others to move to new areas.
Climate change is also causing the weather to become more extreme. This can make it difficult for butterflies to survive, especially during the winter months.
Understanding the parts of a butterfly diagram is crucial for students preparing for the Big ABA Exam. Refer to the Big ABA Exam Study Manual for comprehensive guidance. By studying the diagram, you can gain insights into the butterfly’s anatomy, including its wings, antennae, and proboscis.
This knowledge is essential for the exam and for understanding the life cycle and behavior of butterflies.
Butterfly Conservation
Butterflies are an important part of our ecosystem, and their populations are facing a number of threats. Conservation efforts are essential to protect these beautiful and beneficial creatures.
One of the biggest threats to butterflies is habitat loss. As humans develop more land for agriculture, housing, and other purposes, butterflies lose the places they need to live and breed. Pesticides and herbicides can also harm butterflies, as can climate change.
Butterfly conservation is important for a number of reasons. Butterflies are pollinators, and they play a vital role in the reproduction of many plants. They are also a food source for other animals, such as birds and bats. In addition, butterflies are simply beautiful creatures that bring joy to many people.
Conservation Efforts
There are a number of things that can be done to help conserve butterfly populations. One important step is to protect and restore butterfly habitats. This can be done by creating butterfly gardens, planting native plants, and reducing the use of pesticides and herbicides.
Another important step is to educate people about the importance of butterflies. By raising awareness about the threats facing butterflies, we can encourage people to take action to protect them.
Clarifying Questions
What are the main body parts of a butterfly?
The main body parts of a butterfly include the head, thorax, abdomen, antennae, and legs.
How do butterflies communicate with each other?
Butterflies communicate through visual cues, chemical signals, and tactile interactions.
What factors influence butterfly development?
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability influence butterfly development.